By Kathleen Corcella and Bethany Anderson
Thousands of dots swirled across a computer screen. These scientific data points would soon be transformed into a mesmerizing film for the large screen. This is but one example of the many scientific visualizations created by Donna J. Cox, Michael Aiken Chair Emerita, Professor Emerita of Art and Design, and former Director of the Advanced Visualization Laboratory (AVL) at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA). Projects like this are documented in Cox’s recently donated papers, which are now available for research use.
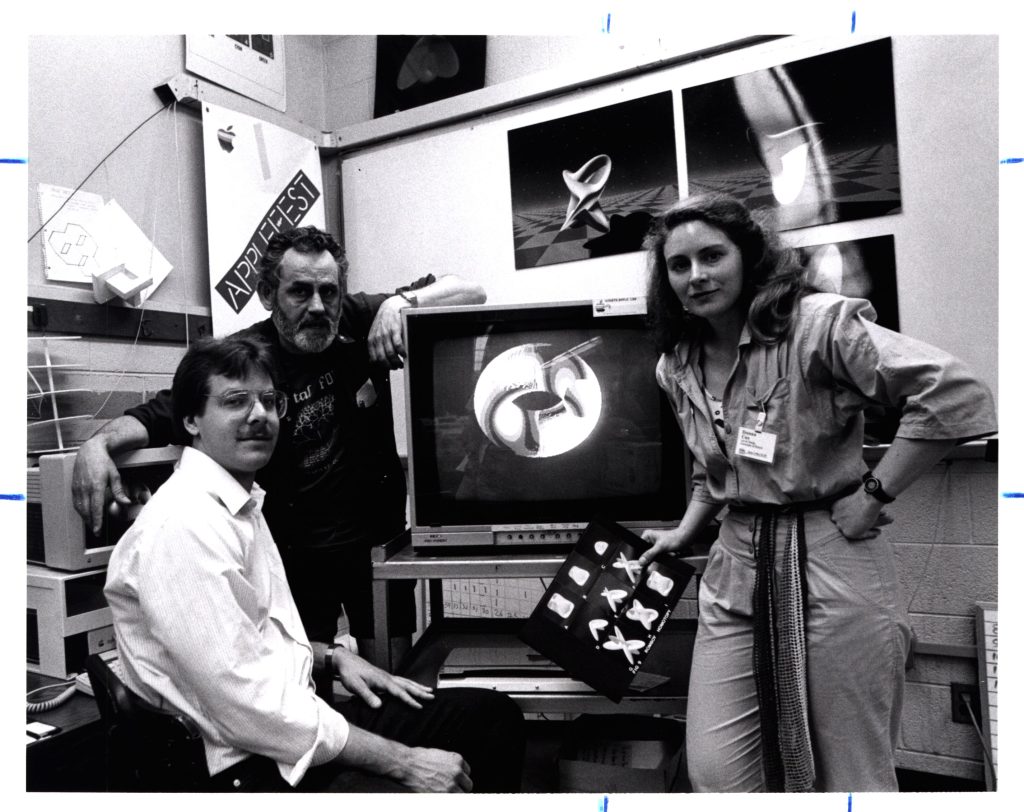

Cox is renowned for bridging both art and science in her work and for innovating the creation of scientific visualizations and collaborative interdisciplinary teams. Cox and the AVL have created visualizations that have garnered numerous accolades, including an Academy Award nomination. Hailing from Enid, Oklahoma, Cox cites her upbringing by her mother and grandmother, “two strong, determined women,” as instrumental and inspirational to her pursuit of science and art. [1] Following the death of her father during World War II, her mother and grandmother raised Cox and brother, working day and night shifts respectively: “Their perseverance inspired me to take risks and make the most out of life, regardless of the odds, exhibiting the power of women and collaboration.” [1] In 1967, Cox became the first individual in her family to graduate from high school. Following graduation, she moved to Denver, Colorado, and eventually to Seattle, Washington, where she worked in the corporate sector.
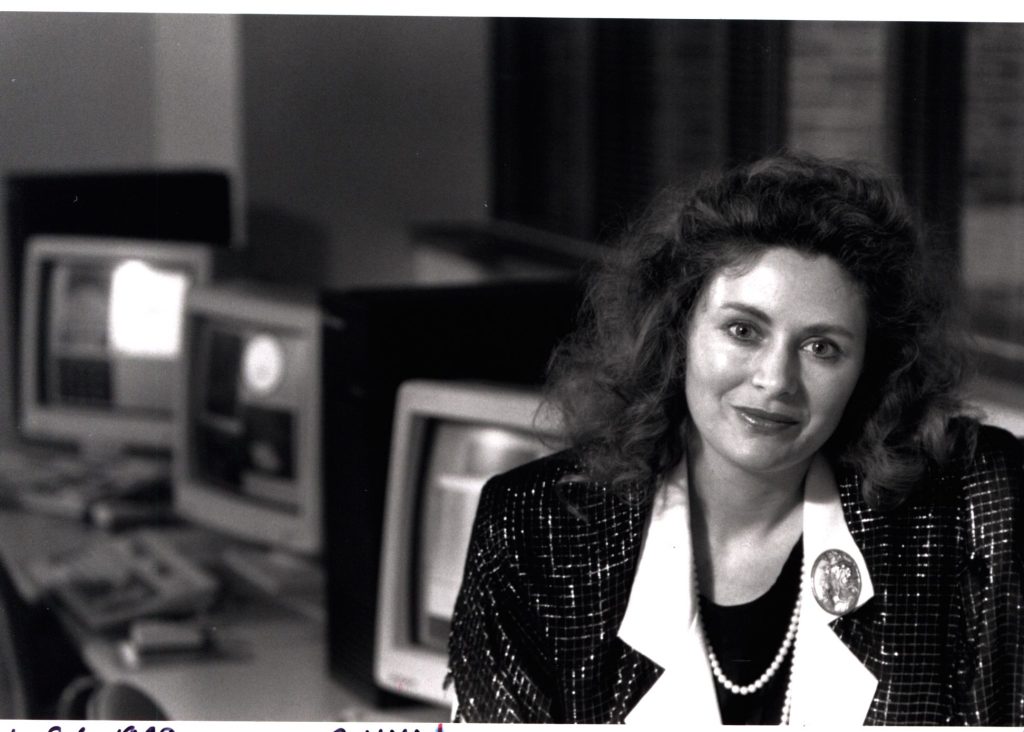

Cox left her job and enrolled full-time at the University of Wisconsin-Madison where she earned a bachelor of arts (1982) and a master of fine arts (1985). [1] While at U-W Madison, Cox met several people who would influence the trajectory of her career, including fellow student Pat Hanrahan. Hanrahan introduced Cox to computer graphics and gave her code he developed for color displays on campus. Cox was inspired by the possibilities of technology and learned how to create computer graphics and programs and created 2-D imaging software. [2] Cox also met Professor Dan Sandin from the School of Art and Design at the University of Illinois Chicago, who was visiting U-W Madison to give a guest lecture. During his visit, Sandin toured the computer lab where Cox created the Interactive Computer Assisted RGB Editor (ICARE), a digital tool for color images and mapping. [2] Sandin was impressed with Cox’s work and introduced her to the Electronic Visualization Lab (EVL) in Chicago.
In 1985, Cox accepted a position at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign as a visiting assistant professor of art and design. Prior to coming to Illinois, Cox developed the idea of a “Renaissance Team” to describe a group of individuals from a variety of disciplines who work together to achieve a common goal. [2] During her time at NCSA and tenure as Director of the AVL, Cox employed this concept to the formation of collaborative projects.
At the urging of her grad advisor, Cox reached out to NCSA founding director, Larry Smarr, after learning about the new supercoming center. [1] Smarr invited Cox to one of the opening events for the new NCSA, where she showcased her computer collages (called “compulages”) and advocated for collaborations between artists and scientists to visualize data. [4] Smarr appointed Cox as a faculty affiliate at the NCSA. It was during this time that Cox launched a scientific visualization program, drawing on collaborations formed with the EVL in Chicago and other Renaissance Teams that she created for various projects.
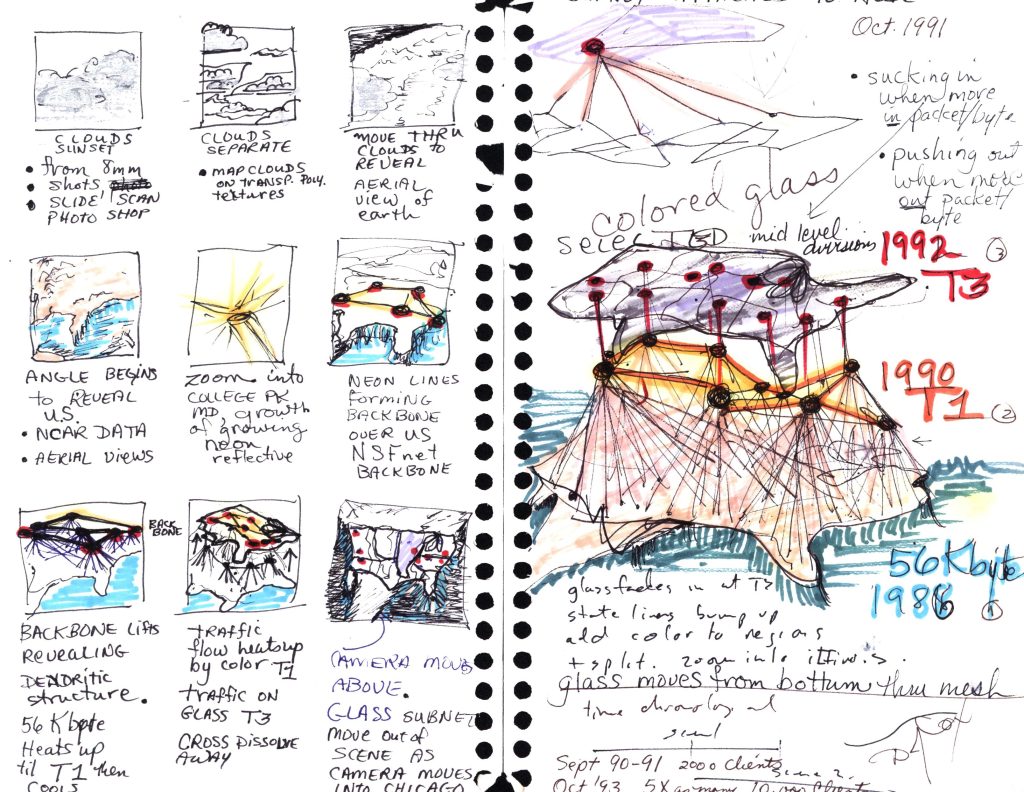
Cox worked on many computer graphic arts and visualization projects while at the NCSA and through her involvement in the Association for Computing Machinery’s (ACM) Special Interest Group on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH). These projects include NSFNet, a visualization of the early internet, and Venus, a series of abstract conceptualizations of the Paleolithic female figure Venus of Willendorf rendered two-dimensional for display on a computer screen, which Cox created as a tribute to her grandmother, Sadie Elmo. [3] Cox also illustrated the capabilities of NCSA’s supercomputers and visualizations through a remote-control demonstration at the SIGGRAPH 1989 Boston conference. In addition, the work of Cox and the AVL has appeared in several films and documentaries, including Cosmic Voyage (1997), Hubble 3D (2010), and The Tree of Life (2011). Notably, these projects use real scientific data and cinematic computational science as a method for creating visualizations. Cox has won numerous awards for her work, and in 2006 was selected as one of forty modern-day Leonardo da Vincis by the Museum of Science and Industry in Chicago.

Donna J. Cox’s innovative work illustrates the ways in which art and science can be powerfully fused. Cox’s papers in the University Archives are an important source for engaging with and studying her work and contributions. These materials include original storyboards and notes documenting Cox’s creative process, correspondence with colleagues relating to digital arts and various projects, copies of media features and interviews with Cox, photographs and slides of works, awards, and more. Beyond her papers, researchers can learn more about her career and experiences through her talk in 2023 for the Archives’ Women in Science Lecture Series (recording is available here). For questions or more information about Donna J. Cox’s papers, please contact Bethany Anderson, bgandrsn@illinois.edu.
[1] Bui, S. A. (2021, July 30). The Donna Cox Legacy: Inspiring and Visualizing the Future. NCSA. https://www.ncsa.illinois.edu/the-donna-cox-legacy-inspiring-and-visualizing-the-future/.
[2] Cox, D.J., Sandor, E., Fron, J. (Eds.). (2018). New media futures: The rise of women in the digital arts (pp. 71-84). Urbana: University of Illinois Press.
[3] Cox, Donna J., Press Releases (Public Affairs Office), Record Series 39/1/10, University of Illinois Archives.
[4] This idea is described in Donna Cox’s article, “Using the Supercomputer to Visualize Higher Dimensions: An Artist’s Contribution to Scientific Visualization,” Leonardo 21, no. 3 (1988): 390-400, https://doi.org/10.1162/leon.2008.41.4.390; see also in box 10, Donna J. Cox Papers, Record Series 7/5/20, University of Illinois Archives.




